
In the fast-paced world of eCommerce, businesses face an ongoing battle against fraudsters who continuously evolve their tactics to exploit vulnerabilities in the system. Two relatively recent techniques in the email-based fraud are Plus Addressing Fraud and Dot Addressing Fraud. This article aims to explain both of these methods and provide strategies to against these threats.
What is Plus Addressing Fraud
Plus Addressing Fraud is a relatively new method used by cyber criminals to manipulate email addresses for malicious purposes. In standard email addressing, the plus (+) symbol is a valid character that can be utilized to create an unique email address.
For example, if a user’s primary email address is johndoe@example.com, they can generate aliases like johndoe+newsletter@example.com or johndoe+support@example.com. These aliases are all directed to the user’s main inbox.
Fraudsters exploit this system by creating multiple accounts using slight variations of their email addresses, making it challenging for businesses to detect fraudulent activity. They can register with an eCommerce site using the email address johndoe+1@example.com and then create another account like johndoe+2@example.com. To the eCommerce platform, these addresses appear as distinct, separate users, even though they ultimately lead to the same individual.
What is Dot Addressing Fraud
Dot Addressing Fraud is another ambiguous email tactic used by cyber criminals. Instead of using the plus symbol, fraudsters manipulate email addresses by inserting extra dots (.) within the email address.
For example, if the legitimate email address is johndoe@example.com, fraudsters may create aliases like j.ohndoe@example.com or jo.hndoe@example.com. These variations can appear as distinct email addresses to systems that do not account for dot placement.
Dot Addressing Fraud is less common than Plus Addressing Fraud, but it can be equally challenging to detect. It operates on the principle that email systems often ignore the placement of dots within the local part of the email address, causing them to be delivered to the same inbox.
How to Prevent Plus & Dot Addressing Fraud using FraudLabs Pro
In order to mitigate the risk of Plus Addressing Fraud and Dot Addressing Fraud, FraudLabs Pro has introduced a functionality known as “Email Sanitization“. This feature empowers merchants to inspect and prevent fraudulent activities effectively. By embracing this capability, businesses can strengthen their defenses against addressing fraud and reinforce the security of their transactions. Please note that it is exclusively available to merchants who are subscribed to the Small plan or higher.
Enable The Email Sanitization Feature
The steps below show how to enable the Email Sanitization feature:
- Login to the merchant area.
- Go to Settings.
- Under the Customer Management section, click on the Enable Email Sanitization for Plus Addressing and Dot Addressing.
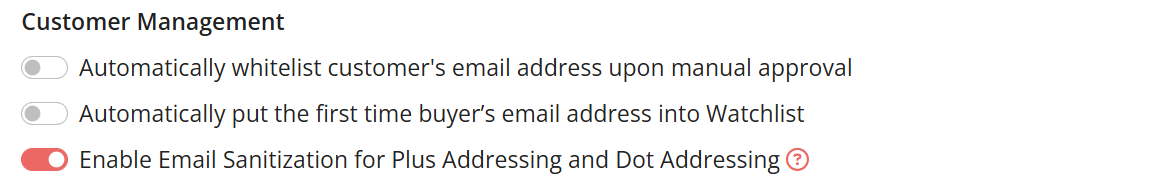
- Click on Save Changes.
- Done.
Upon activating the Email Sanitization feature, a cautionary signal will be visibly presented on the transaction page, serving as an alert that the system has detected the presence of multiple forms of Plus Addressing or Dot Addressing. This visual indicator is a proactive measure to keep merchants informed about potential irregularities in the email addresses provided during transactions.
Follow steps below to view the warning indicator:
- Login to your merchant area.
- Go to Transactions, then click on one of the transaction detail.
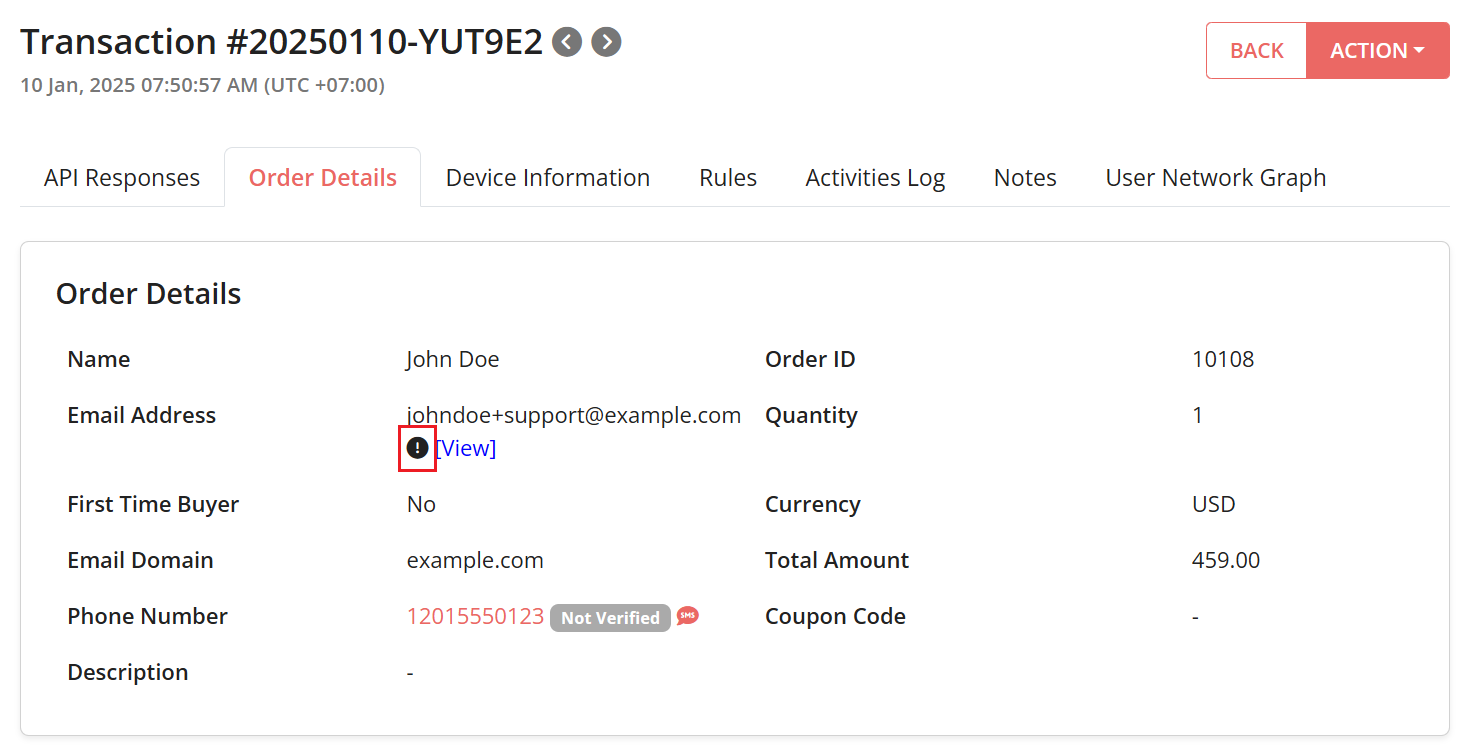
- Go to Order Details tab.
- Under Email Address, you will see a warning indicator beside the email address if the email has more than one type of Plus Addressing or Dot Addressing.
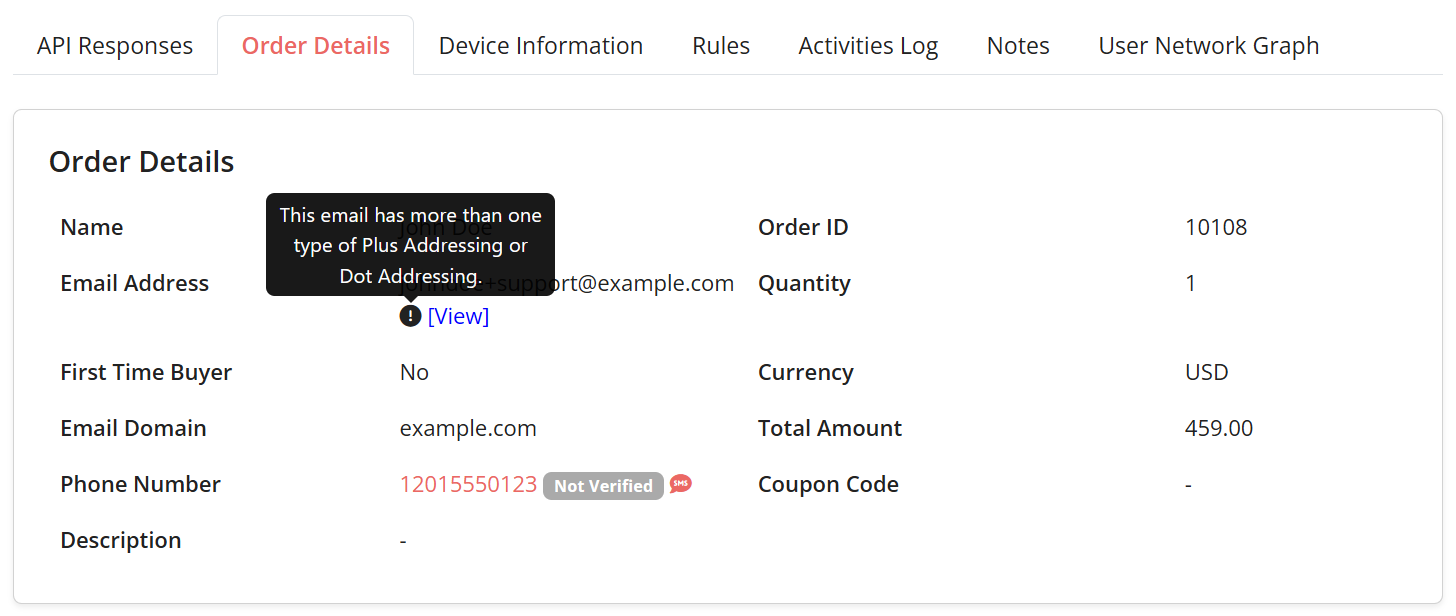
5. Just hover the indicator, you will see the message.
Configure Fraud Validation Rules
Furthermore, when the Email Sanitization feature is enabled, FraudLabs Pro will employ the sanitized email for a comprehensive examination against all relevant velocity rules associated with email addresses.
You can configure velocity rules to ensure that potential risks tied to email addresses are thoroughly assessed, enhancing the system’s ability to detect and prevent fraudulent activities effectively.
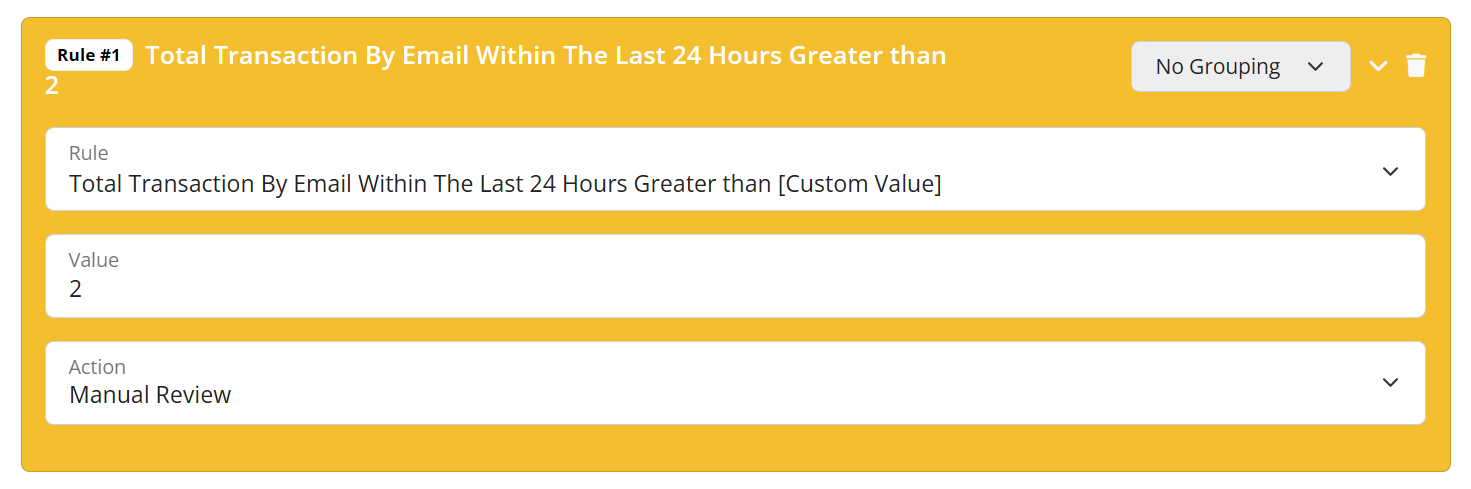
Examples of these velocity rules that can used are:
- Total Transaction By Email Greater/Less than [Custom Value]

- Total Transaction By Email Within The Last 24 Hours Greater/Less than [Custom Value]
- and etc.
Conclusion
In a nutshell, fraudsters are continually evolving their tactics to exploit system vulnerabilities in the world of eCommerce. Plus Addressing Fraud and Dot Addressing Fraud are two relatively new methods that pose significant challenges to online businesses. By understanding these tactics and implementing preventative measures, eCommerce platforms can safeguard themselves against malicious activities that can harm their reputation and profitability. Preventing Plus Addressing Fraud and Dot Addressing Fraud requires vigilance and a proactive approach, ensuring a secure and trustworthy online shopping environment for all customers.
Secure Transactions, Seamless Business
Say goodbye to fraud worries! Secure your online store with FraudLabs Pro now.