In the world of internet connectivity, there are two primary versions of the Internet Protocol (IP) that enable communication between devices: IPv4 (Internet Protocol version 4) and IPv6 (Internet Protocol version 6). These protocols define data transmission over networks and assign unique IP addresses to devices. As the demand for internet usage continues to rise, the transition from IPv4 to IPv6 has become necessary due to the limited number of available IPv4 addresses.
The above is the technical brief of IPv4 and IPv6, but does it matter for a merchant to know these technologies and the differences? No, at least not to have an in-depth understanding of this jargon, but it’s good to have a general understanding of IPv4 and IPv6.
IPv4: The Current Standard
IPv4 has a long history of use on the internet and remains prevalent even today. It uses a specific format (32-bit address format) to assign a unique address to each device connected to the internet. However, there are only a limited number of these addresses available, approximately 4.3 billion IP addresses, and with the increasing number of internet-connected devices, we are running out of them. This means that it is becoming more difficult for new devices to get their own unique address.
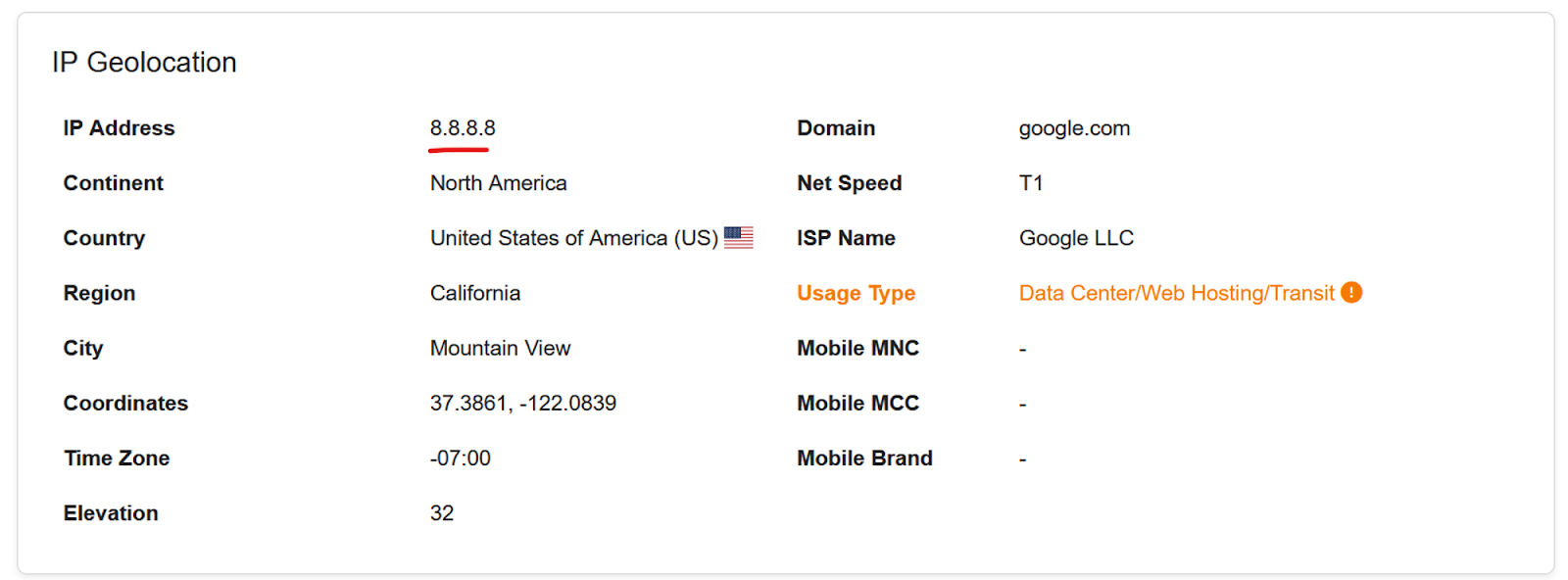
What does an IPv4 address look like? An IPv4 address is represented in a dotted decimal notation consisting of four sets of values ranging from 0 to 255, separated by dots. The minimum IPv4 address is 0.0.0.0, and the maximum is 255.255.255.255. Below is an example of an IPv4 address that you can find inside the FraudLabs Pro transaction details page.
IPv6: The Internet’s Future
From the above paragraph, it is evident that the depletion of IPv4 addresses is an issue, and a larger and future-proof solution is needed to overcome internet connection problems. This is the reason why IPv6 was developed, with the goal of addressing the limitations of IPv4 and providing a solution for the increasing demand for IP addresses. Unlike IPv4, IPv6 uses a 128-bit address format, which allows for an almost unlimited number of unique IP addresses. To provide you a clear picture, it offers approximately 340 trillion trillion trillion (or 340 undecillion) IP addresses, providing the capacity to accommodate the ever-growing number of devices such as smartphones, tablets, IoT devices, and more. It is an incredibly vast capacity.
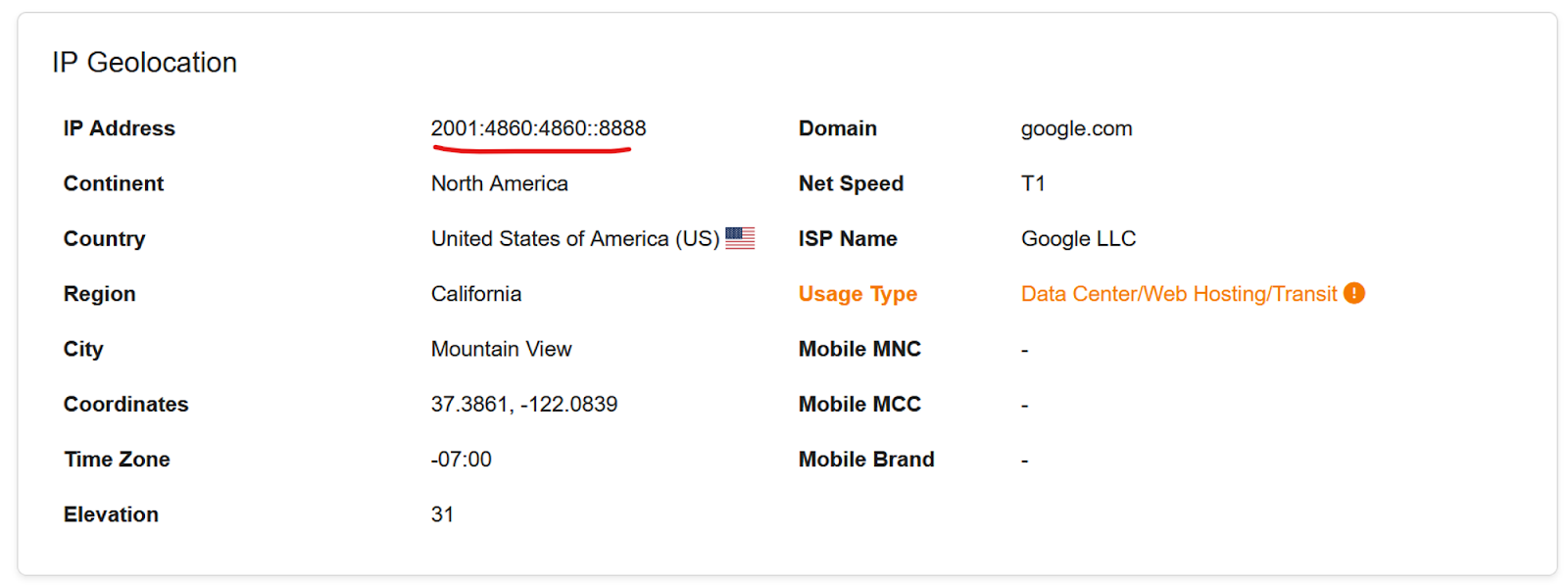
What does an IPv6 address look like? An IPv6 address is represented in a hexadecimal notation consisting of eight sets of four hexadecimal digits, separated by colons. The minimum IPv6 address is 0:0:0:0:0:0:0:0, and the maximum is ffff:ffff:ffff:ffff:ffff:ffff:ffff:ffff. IPv6 addresses are much longer and provide a significantly larger pool of unique addresses compared to IPv4. Below is an example of an IPv6 address that you can find inside the FraudLabs Pro transaction details page. Please note that the double colon (::) is a type of compression in IPv6.
Impact on E-Commerce Websites
There is no real impact on your e-commerce website from the perspective of internet connectivity and website hosting. This is because most servers are now IPv6 ready, and if not, the IPv4-IPv6 tunneling should have been properly set up. This means that regardless of the visitor’s IP version, the connection is managed seamlessly behind the scenes.
From the viewpoint of fraud detection, the IP address is crucial as it provides several important pieces of information. This includes the approximate location of the buyer, whether they are browsing using an anonymous proxy, if they keep changing IP addresses, and more. However, you also don’t need to worry about the IP address formatting. It is properly handled and translated into readable and actionable information on the FraudLabs Pro transaction details page. The IP address is simply a technical representation, but you should focus more on the derived information for your analysis or necessary actions.
However, there are certain scenarios where you may need to use the IP address to help mitigate fraud cases. One such scenario is the IP blacklist. If you observe excessive abnormal purchases from a single IP address, or if you have a list of suspicious IP addresses that you want to blacklist, then under such circumstances, you may need the IP address to manually add them into the FraudLabs Pro blacklist database so that the system can automatically cancel their orders. For more information on how to add the blacklist, you can visit the How to add the blacklist article.
To fully restrict user access, you can add their IP addresses to your web hosting site’s Access Control List (ACL). By doing so, you can block the traffic before it reaches your website. However, we won’t delve into ACL details but offer a basic understanding of blocking users via IP addresses.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding IPv4 and IPv6 distinctions is not so crucial for merchants to operate their e-commerce websites. The transition from IPv4 to IPv6 is necessary due to the limited number of available IPv4 addresses. When it comes to fraud detection, the IP address plays a crucial role in providing important information, such as the approximate location of the buyer and whether they are using anonymous proxies. But you should focus on the derived information from IP addresses. Anyway, understanding IP addresses and how to use derived information is beneficial for e-commerce protection.
Free Fraud Protection Today!
Start safeguarding your business with FraudLabs Pro Fraud Prevention at Zero Cost!